Home >>Information Security Cyber Law Tutorial >Intellectual Property Right
Intellectual Property Right
Intellectual Property Right
Intellectual property rights are the legal rights that cover the privileges granted to those who are the owners and inventors of a work, who through their intellectual creativity have created something. Such rights can be given to individuals connected to fields such as literature , music, invention, etc., which can then be used by them in corporate practices.
Without his / her prior knowledge, the creator / inventor obtains exclusive rights against any misuse or use of work. However, to preserve equilibrium, rights are given for a limited period of time.
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) has laid down the following list of activities protected by intellectual property rights -
- Industrial designs
- Scientific discoveries
- Protect against unfair competition
- Works that are literary, artistic, and scientific
- Inventions in all human activity fields
- Artist performances, phonograms, and broadcasts
- Trademarks, marks of service, trade names and designations
- All such rights arising from intellectual involvement in the fields of industry, science, literature, or art
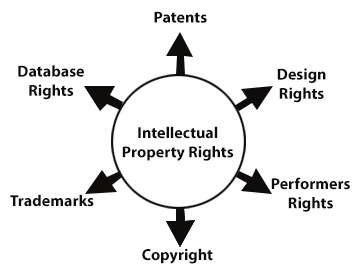
Types of Intellectual Property Rights
It is possible to further classify intellectual property rights into the following categories :
- Copyright
- Patent
- Trade Secrets, etc.
Advantages of Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property rights are useful in the following respects :
- Provides the creators or inventors with exclusive rights.
- Instead of keeping it confidential, allow people to distribute and share information and data.
- It provides legal protection and provides the creators with the opportunity to work.
- Helps to develop socially and financially.
Intellectual Property Rights in India
India has defined the establishment of a constitutional , administrative and legal outline in order to protect intellectual property rights in the Indian territory, whether they include copyright, patents, trademarks , industrial designs or some other part of intellectual property rights.
Back in 1999, in order to protect intellectual property rights, the government passed an important law focused on international practices. Let us get a glimpse of the same thing.
- The Patents ( Amendment) Act , 1999, facilitates the establishment of a patent filing mail box system. It provides exclusive marketing rights for a five-year term.
- The Trade Marks Act, 1999, replaced the 1958 Trade and Merchandise Marks Act.
- The Copyright ( Amendment) Act, 1999, was signed by India 's President.
- The law of sui generis was introduced and named as the Bill on Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection), 1999.
- The Designs Act, 1911, was replaced by the Industrial Designs Bill, 1999.
- The Patents (Second Amendment ) Bill, 1999, for further amendment in accordance with the TRIPS of the Patents Act of 1970.
Intellectual Property in Cyber Space
A variety of threats are faced by any new innovation in the field of technology. One such challenge is the Internet, which has taken the physical marketplace and made it a virtual marketplace.
It is necessary to establish an efficient property management and protection mechanism in order to safeguard the business interest, taking into account the considerable amount of business and commerce taking place in the cyber space.
Today, creating an efficient and collaborative IP management mechanism and protection strategy is essential for any enterprise. In the cybernetic world, the ever-looming threats can thus be monitored and confined.
The lawmakers have designed various approaches and legislation to up the ante in providing a secure configuration against such cyber threats. However, by taking proactive measures, it is the responsibility of the intellectual property right (IPR) owner to invalidate and reduce certain mala fide actions by criminals.
